
The N shell containing 4s, 4d, 4p and 4f, can carry 32 electrons.
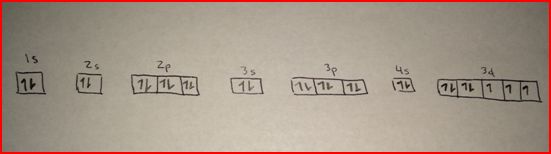
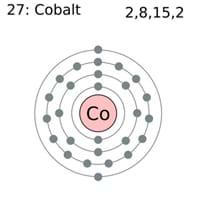
The M shell contains 3s, 3p, and 3d, and can carry 18 electrons. The K shell contains a 1s subshell hence it can carry 2 electrons, the L shell has 2s and 2p, and can carry 8 electrons. This decides the electron capacity of the shells. The maximum electrons that can be carried by the sub-shell S is 2, by P is 6, by D is 10, and the F sub-shell can carry 14. Each shell and subshell have a limitation on the amount of electrons that it can carry. Electronic configuration: In an electronic configuration, electrons are distributed in different atomic or. The subshells have a distinct shape and configuration, in which the electrons move freely. Cobalt - Element information, properties and uses Periodic Table Glossary Allotropes Some elements exist in several different structural forms, called allotropes. The electron configuration is Ar 3 d 7 4 s 2.
#COBALT AND CHROMIUM ELECTRON CONFIGURATION FULL#
In these cases, a completely full or half full d sub-level is more stable than a partially filled d sub-level, so an electron from the 4s orbital is excited and rises to a 3d orbital. They stand for sharp (S), principal (P), diffuse (D), and fundamental (F). There are two main exceptions to electron configuration: chromium and copper. The shells are labeled K, L, M, N, and so on, from the innermost to the outermost shell.Įach shell has subshells that are named for the type of emission lines produced from different states of angular momentum. This model has been widely accepted, and according to it, each atom has shells, which further have subshells. They are usually anions or polar molecules. Complexes Ligands The molecules or ions coordinating to the metal are the ligands. Compounds containing complexes are coordination compounds. It involves the specific arrangement of electrons in shells and sub-shells of Bohr’s atomic model. A central metal atom can bond to a group of molecules or ions: metal complex. The concept of electronic configuration has replaced the older concept of valency and valence electrons. The Aufbau principle says the first two electrons would fill the 1s orbital. For example, oxygen has eight protons and eight electrons.

n is the energy level O is the orbital type (s, p, d, or f) e is the number of electrons in that orbital shell. The equation is: 1s<2s<2p<3s<3p<4s<3d<4p<5s<4d<5p<6s<4f<5d<6p<7s<5f<6d<7p The notation seen on period tables for electron configurations uses the form: nO e. The electronic configuration of each element is decided by the Aufbau principle which states that the electrons fill orbitals in order of increasing energy levels.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
